IB Chemistry,Uncertainty, Error Analysis, Standard Deviation
Uncertainty Calculation for Rate and Concentration of reaction.
Rate = 1/time, Time for X to disappear. ( Iodine Clock Reaction)
3 Methods for Uncertainty Calculation for Rate (0.10M) KI.
Average time is (5.28 + 4.75 + 4.47) / 3 = 4.83
1) % Uncertainty Method
- Uncertainty time = Uncertainty stop watch + reaction time, ( 0.01 + 0.09 ) = ( 0.10 )
- Time = 4.83 ±( 0.10 )
2) Max-min range Method
- Uncertainty time = (Max time - Min time)/2, = ( 5.28 - 4.47 )/2 = 0.41
- Time = 4.83 ±0.41
1) %Uncertainty Method
Uncertainty time = (4.83 ± 0.10)
Rate = 1/ time, 1/4.83 = 0.207
2) Max-min range Method
Uncertainty time = ( 4.83 ± 0.41)
Rate = 1/time, 1/4.83 = 0.207
1) % Uncertainty Mtd
%Uncertainty time = (0.1/4.83) x100 %=2.07
%Uncertainty Rate = %Uncertainty time
%Uncertainty Rate = 2.07%
Rate = 0.207 ± 2.07 %
Rate = 0.207 ± 0.004
2) Max-min range Method
% Uncertainty time = (0.41/4.83) x 100% = 8.48%
% Uncertainty Rate = % Uncertainty time
%Uncertainty Rate = 8.48%
Rate = 0.207 ± 8.48%
Rate = 0.207 ± 0.017
3) Max /Min Rate Method
3) Max /Min Rate Method
Max Rate = 1/Minimum time, 1/4.47 = 0.220
Min Rate = 1/Maximum time, 1/5.28 = 0.190
Ave rate = 1/ Ave time, 1/ 4.83 = 0.207
Uncertainty Rate = 0.207 ± ( 0.220 --- 0.190 )
.........................................................................
Uncertainty Cal for Conc, 30ml 0.1M KI (2 Methods used)
1) % Uncertainty Method
Pipette uncertainty = ± 0.4 and Total Volume used = 30ml
1) % Uncertainty Method
%Uncertainty Conc = %Uncertainty Vol of KI + %Uncertainty Vol Water
%Uncertainty Vol KI = (0.4/30) x100%=1.3%
%Uncertainty Conc = % Uncertainty Vol KI
%Uncertainty Conc = 1.3%
Calculation Absolute Uncertainty
Conc = 0.10 ± 1.3%
Conc = 0.100 ± 0.001
......................................................................
2) Max/Minimum Method
Preparing 0.053M from 0.1M KI using pipette.
Pipette uncertainty = ± 0.4
Max Conc KI = Max Vol KI and Min Vol of water used
M x V (dil) = M x V (conc)
M x (15.8 + 14.2) = 0.1 x (15.8)
M = 0.1 x ( 15.8 )/( 15.8+ 14.2 )
M = 0.053
Max Conc KI=Max Vol KI + Min Vol water
Max Vol KI = 15.8 ± 0.4 = 16.2
Min Vol water = 14.2 ± 0.4 = 13.8
M x V (dil) = M x V (conc)
Max Conc KI = (0.1 x 16.2)/ ( 16.2 + 13.8 )
Max Conc = 0.054
Min Conc = Min Vol KI and Max Vol water used
Min Vol KI = 15.8 ± 0.4 = 15.4
Max Vol water = 14.2 ± 0.4 = 14.6
M x V (dil) = M x V (conc)
M x (15.4 + 14.6) = 0.1 x (15.4)
M = 0.1 x ( 15.4 )/( 15.4 + 14.6 )
M = 0.051
Min Conc = 0.051
Uncertainty Conc = 0.053 ± ( 0.054 --- 0.051)
..................................................................................................................................................
Uncertainty Cal, 2 fold Serial dilution using 3% H2O2
2 Methods using
1st % Uncertainty Method
For 1.5%, Total % Uncertainty is 1.6%, Answer = 1.5 ± 1.6%, Propagation of error involved
Absolute Uncertainty for 1.5 ± 1.6% = (1.50 ± 0.02)%
.......................................................................................................................................................
2nd, Max/ Min Method
For 2 fold Serial dilution on 3% H2O2
M x V (dil) = M xV (conc)
M x (1.5 +1.5) = 3% x 1.5
M = 1.5%
Max Conc H2O2 when
Max Vol H2O2 used = 1.51
Min Vol water used = 1.49
Min Conc H2O2 when
Min Vol H2O2 used = 1.49
Max Vol water used = 1.51
Max Conc H2O2 Min Conc H2O2
M x V (dil) = M x V (conc) M x V (dil) = M x V (conc)
M x (1.51 + 1.49) = 3% x ( 1.51 ) M x (1.51 + 1.49) = 3% x ( 1.49 )
M = 3% x ( 1.51 )/( 1.51 + 1.49 ) M = 3% x ( 1.49 )/( 1.51 + 1.49 )
M = 1.51% M = 1.49%
Max Conc = 1.51% Min Conc = 1.49%
Uncertainty Conc H2O2 = 1.50 ± (1.51%---1.49%)
......................................................................................................................................................
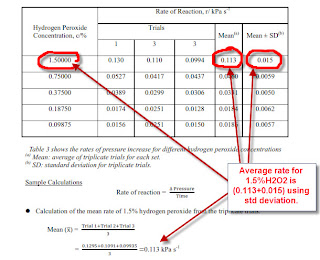
Uncertainty Cal for Rate Using Vernier Sensor.
How changing conc of H2O2 affect the rate of decomposition of H2O2 (catalase) measured using pressure sensor?
Initial Rate for 1.5% = slope/ gradient of curve
Perform 3 trials at 1.5% and take Average rate
Average Rate by taking average for 3 trials
Uncertainty for Rate = Standard deviation
Use Excel to calculate Std deviation
........................................................................
Video on adding Std deviation into Excel
......................................................................................................................................................
IB Chemistry, Enthalpy, Uncertainty Calculation, Error analysis, Standard Deviation
Enthalpy change for displacement Zn + CuSO4
2 methods for Uncertainty Cal
1) % Uncertainty Method
Zinc excess, Copper limiting,
Conc CuSO4 = (1M± 0)
Vol = (20.0 ± 0.3) ml
Mol of Cu ions= M x V= 0.02 mol
△t = (68.0±0.2) - (25.1±0.2) = (42.9±0.4)
m = 20.0 ± 0.3ml
Q = mc△t
Q = 20.00 x 4.184 x △t
Q = 20.00 x 4.184 x 42.9
Q = 3589.8J ----------0.02 mol
Q = 3589.9/0.02------ 1mol
Q = 179.5kJ/mol
Extrapolation for Temp increase, 68.0 - 25.1= 42.9
%Uncertainty Q = % Uncertainty m + % Uncertainty △t
%Uncertainty m = (0.3/20) x 100% = 1.5%
%Uncertainty △t = (0.2+0.2) / 42.9 x 100% = 0.93%
%Total Uncertainty = (0.93 + 1.5) = 2.43%
Q = (179.5 ± 2.43%)
Q = (179.5 ± 4.36) = (180 ± 4)kJ/mol
2) Using Max/Min Method
Q = mc△t
Q = 20.00 x 4.184 x 42.9
Q = 3589.8J ----------0.02 mol
Q = 3589.9/0.02------ 1mol
Q = 179.5kJ/mol
Q = mc△t
△t = 42.9 ± (0.2+02) = (42.9±0.4) max t= 42.9+ 0.4 = 43.3 min t=42.9- 0.4=42.5
m = 20.0 ± 0.3ml max m= 20.0+ 0.3=20.3 min m=20.0- 0.3= 19.7
Max △ Q = Maximum △ m and Maximum △t
Max △ Q = m c△t = 20.3 x 4.184 x 43.3 = 3677.7J
Max Q = 3677.7J -----------0.02mol
Max Q = 3677.7/0.02-------1 mol
Max Q = 183.3kJ/mol
Min △Q = Minimum △ m and Minimum △t
Min △Q = mc△t = 19.7 x 4.184 x 42.5 = 3503.0J
Min Q = 3503.0J------------0.02mol
Min Q = 3503.0J/0.02-------1 mol
Min Q = 175.1kJ/mol
Using Max/Min Method Using %Uncertainty Method
Q = 179.5 ± ( 183.3--175.1)kJ/mol Q = (179.5 ± 2.43%) = (180 ± 4)kJ/mol
Q = (183.3---175.1) Q = (184---176)
..................................................................................................................................................
Accurate way taking Uncertainty Moles Cu
1) Using %Uncertainty Method.
%Uncertainty moles of Cu used
Conc CuSO4 = (1M±0) , Vol = (20.0 ± 0.3) ml
Moles of Cu ions = M x V= 0.02 mol
%Uncertainty moles Cu = %Uncertainty in M + %Uncertainty in Vol
%Uncertainty Cu = 0% + (0.3/ 20) x 100% = 0% +1.5% = 1.5%
Total %Uncertainty Q = %Uncertainty m + %Uncertainty △t + %Uncertainty mol Cu
Total %Uncertainty Q = 1.5% + 0.93% + 1.5% = 3.93%
Q = (179.5 ± 3.93%)= (179.5 ± 7.05) = (179 ± 7)
Q = ( 186 ----172 )kJ/mol
2) Using Max/Min Method
Conc CuSO4 = (1M±0) , Vol = (20.0 ± 0.3) ml
Moles of Cu ions = M x V = 0.02 mol
△t = 42.9 ± (0.2+02) = (42.9±0.4) max t=42.9+0.4 = 43.3 min t=42.9- 0.4=42.5
m = 20.0 ± 0.3ml max m=20.0+ 0.3=20.3 min m=20.0- 0.3= 19.7
Max Vol = 20.3ml, Min Vol = 19.7ml Molarity = (1M±0)
Max moles Cu = Max M x Max Vol = 1 x 20.3 = 0.0203
Min moles Cu = Min M x Min Vol = 1 x 19.7 = 0.0197
Uncertainty moles of Cu 0.020 ± (0.023--0.0197)
Max Uncertainty Q = mc△t = 20.3 x 4.184 x 43.3 = 3677.7J
Min Uncertainty Q = mc△t = 19.7 x 4.184 x 42.5 = 3503.0J
Max Q = 3677.7J ----------0.02mol
Min Q = 3503.0J-----------0.02mol
Uncertainty moles of Cu 0.02 ± (0.023--0.0197)
Max moles Cu = 0.023
Min moles Cu = 0.0197
Max Q = Max Uncertainty Q + Min Uncertainty mol Cu ( will give greatest error )
Min Q = Min Uncertainty Q + Max Uncertainty mol Cu ( will give least error )
Max Q = 3677.7---------------0.0197 mol Cu Min Q = 3503.0---------------0.023mol Cu
Max Q = 3677.7/0.0197-------1 mol Min Q = 3503.0/0.023--------1mol
Max Q = 186.7kJ/mol Min Q = 152.3kJ/mol
Q = 179.5 ± ( 186.7---152.3 )kJ/mol
%Uncertainty Method Max/Min Method
Q = ( 186 ----172 )kJ/mol Q = ( 186.7---152.3 )kJ/mol
..................................................................................................................................................
IA must be done with minimum 3 trials, for valid conclusion.
Displacement done with 3 trials.
Displacement of Zinc + CuSO4
Zinc excess, Copper limiting,
Conc CuSO4 = (1M±0)
Vol = (20.0 ± 0.3) ml
Mol of Cu ions= M x V = 0.02 mol
Two Methods used
1st Method
Average Q for 3 trials and using Standard deviation as uncertainty
Temp change for 3 trials
△t1 =( 26.2 ± 0.2)- (21.7± 0.2)=(4.5± 0.4)
△t2 = (26.1 ± 0.2)- (21.6± 0.2)=(4.5± 0.4)
△t3 = (25.8 ± 0.2)-(21.7± 0.2)=(4.1± 0.4)
Q1 = mc△t1 = 20.0 x 4.184 x 4.5 = 376.5
Q2 = mc△t2 = 20.0 x 4.184 x 4.5 = 376.5
Q3 = mc△t3 = 20.0 x 4.184 x 4.1= 343.1
Average Q = (376.5 + 376.5 + 343.1)/3 = 365.4J Uncertainty Q = Standard Deviation Q= (19.28)
Average Q = 365.4J----------0.02 mol Uncertainty Q = 19.28-----------0.02 mol
Average Q = 365.4/0.02------1 mol Uncertainty Q = 19.28/0.02-----1 mol
Average Q = 18.3kJ/mol Uncertainty Q = 0.96kJ/mol
Average Q = (18.3 ± 0.96)kJ/mol
2nd Method
Taking average Temp change
Average Temp data is taken.
Displacement for Zinc + CuSO4
Zinc excess, Copper limiting,
Conc CuSO4 = (1M± 0)
Vol = 20.0 ± 0.3 ml
Mol of Cu ions= M x V = 0.02 mol
△t = (25.7 ± 0.2) - (21.6 ± 0.2)= (4.1 ± 0.4)
By extrapolation using average temp
△t = (25.7 ± 0.2) - (21.6 ± 0.2)= (4.1 ± 0.4)
Q = mc△t
Q = 20.0 x 4.184 x △t
Q = 20.0 x 4.184 x 4.1
Q = 343.1J ---------0.02 mol
Q = 343.1/0.02------1 mol
Q = 17.155kJ/mol
Using %Uncertainty Method
Temp increase = (25.7 ± 0.2) - (21.6 ± 0.2)= (4.1 ± 0.4)
%Uncertainty Q = % Uncertainty m + % Uncertainty △t
%Uncertainty m = (0.3/20) x 100% = 1.5%
%Uncertainty △t = (0.4 / 4.1) x 100% = 9.75%
%Total Uncertainty = (1.5 + 9.75) = 11.25%
Q = (17.155± 11.25%)= (17.15±1.92)kJ/mol
More accurate way is to consider Uncertainty for moles Cu
Conc CuSO4 = (1M± 0), Vol = (20.0 ± 0.3) ml
Mol of Cu ions= M x V
%Uncertainty moles Cu = %Uncertainty in M + %Uncertainty in Vol
%Uncertainty Cu = 0% + (0.3/ 20) x 100% = 0% +1.5% = 1.5%
%Total Uncertainty Q = %Uncertainty m + %Uncertainty △t + %Uncertainty mol Cu
%Total Uncertainty Q = 1.5% + 9.75% + 1.5% = 12.75%
Q = (17.15± 12.75%) = (17.15± 2.18)kJ/mol
You can also use Max/min Method as shown above.
In short,
- Make sure you perform 3 trials and compute the average or use std deviation
- Use %Uncertainty or Max/min Method of your choice
- Use lots of common sense for error treatment
- The only certainty in life is continual uncertainty
- Have fun with uncertainty
.......................................................................................................................................................
Uncertainty Calculation for Rate of reaction, Enthalpy Change and Ideal Gas Equation.
Uncertainty Calculation for RMM using Ideal Gas Equation.
Ideal gas law equation, PV = nRT
Notes for Ideal Gas Equation.
V - volume in m3
n - number of moles
T - absolute temperature.(Kelvin)
R = gas constant, 8.314 J K-1 mol-1
Calculate the RMM of a gas, given
M1, mass empty flask, = (25.385 ±0.001)g
M2, mass flask filled with gas, = (26.017 ±0.001)g
M3, mass flask with water, = (231.985 ±0.001)g
Temperature = 32.0C = (273.0 +32.0) = (305.0 ±0.1)K
Atmospheric pressure = 101,000 Nm-2 /Pa
PV = nRT, n = mass/ RMM
PV = RT x mass/RMM
RMM = RT x mass / PV
Mass of gas = (M2 - M1) = (26.017 - 25.385)g = 0.632g
Vol of gas = Vol of flask = Vol of water = Mass of water = (231.985 - 25.385) = 206.6 x10-6 m3RMM = RT x mass / PV
RMM = 8.314 x 305.0 x 0.632 / 101,000 x 206.6 x10-6
RMM (expt value) = 76.80 RMM (actual value) = 80.00
Percentage Error
= RMM (actual) - RMM (expt) /RMM (actual) x100%
= (80.00 - 76.80)/80.00 x 100%
= 3.20/80 x 100% = 4% (Error)
Percentage Uncertainty due random error ( Temp, Mass and Vol )
% Uncertainty Temp = (0.1/305.0 x 100)% = 0.0327% = 0.33%
% Uncertainty Mass gas = (0.002/0.632 x 100)% = 0.32%
% Uncertainty Vol = (0.002/206.6 ) x 100% = 0.000968% = 0.001%
Total % Uncertainty due to random error = ( 0.33 + 0.32 + 0.001 )% = 0.651% = 0.65%
Conclusion:
- 4% error is more than the total error due to all random error (T, Vol and Mass)
- Systematic error have to account for the 3.35% difference which might be due to experimental procedure.
- RMM = (76.8 ± 0.65%) in percentage uncertainty
- RMM = (76.8 ± 0.5) in absolute uncertainty, max/min range is ( 76.3----77.3)
Determination of (RMM) of a gas ( CO2 or butane ) using ideal gas equation.
Steps to follow
1. Weigh a dry 100ml volumetric flask with stopper to 0.001g
2. Remove stopper
3. Fill it with CO2/butane gas with glass delivery tube, stopper it and reweigh
4. Repeat step 2 and 3 until mass of flask is constant
5. Fill the flask with water, insert a stopper, and reweigh it.
Click HERE for more info on ideal gas equation